Updated on August 12, 2025
Summary
The Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act, 2005, gives daughters equal rights in their father’s property, including ancestral and self-acquired assets. A daughter can claim a share if the father dies without a will, if the property is ancestral, or if she’s named in a valid will.
She can also inherit as an adopted daughter or legal guardian. However, her rights can be denied if there’s a valid will excluding her, a legal partition before 2005, religious conversion (for her descendants), or legal disqualifications. Each case depends on specific conditions, and legal advice is often necessary.
The Hindu Succession Act 1956 tells who can get property in Hindu families. This law also applies to Sikhs Jains and Buddhists. In 2005, the property law changed to give daughters equal rights to their father’s property, just like sons.
But this doesn’t mean a daughter can claim property in every situation. There are specific rules that decide when she can and cannot inherit. This guide breaks it down for you in a simple way.
When Can a Daughter Claim Her Father’s Property?
1. If the Father Dies Without a Will
If the father passes away without writing a will, this is called intestate succession. In this case, the property is divided as per the Hindu Succession Act.
- A daughter gets equal rights like the son.
- She is considered a Class I heir, which includes sons, daughters, a widow (the mother), and a few close relatives.
- The property is divided equally among these heirs.
Example:
If the father leaves behind a wife, one son, and one daughter, the property will be divided into three equal parts—each person gets one-third.
2. If the Property is Ancestral
Ancestral property is passed down through four generations without division. Before 2005, only sons had legal rights in this. But after the 2005 Amendment:
- Daughters became coparceners by birth (meaning they get a share automatically).
- They now have the same rights and responsibilities as sons.
- This includes married daughters as well.
Can a daughter claim ancestral property if the father is still alive?
Yes, she can. The law gives her equal rights by birth, regardless of the father being alive or not.
3. If the Father Made a Will in Her Name
A father can decide what to do with his self-earned property through a will.
- If the will names the daughter as a beneficiary, she has the legal right to claim it.
- Even if others (like sons or the widow) object, she can enforce her right if the will is valid.
Can a daughter challenge a will?
Yes, if:
- The will was made under pressure or force.
- The father wasn’t mentally sound.
- The will was fake or not legally valid.
4. If No Valid Partition Was Done Before 2005
Before the law changed in 2005, only sons had rights to joint family property. But if no legal partition happened before December 20, 2004, the daughter still has a right.
What counts as a valid partition?
- A registered partition deed, or
- A court order dividing the property.
Note: Oral partitions (just verbal agreements) are not valid. So, if there was no proper document, the daughter can still claim her share.
5. If the Father Died After 2005
If the father passed away after September 2005 and the property is joint family or ancestral, the daughter is legally entitled to an equal share—even if the father didn’t leave a will.
This was confirmed by a Supreme Court ruling in 2020, which said daughters have a birthright no matter when their father died.
6. If the Property Was Inherited Without Conditions
If a father inherits property from his parents or ancestors, he can pass it on to his children unless there are legal restrictions.
- If there are no conditions, the daughter has equal rights.
- If there are specific terms attached to the inheritance (like it must go only to male heirs), her claim depends on those terms.
7. If the Daughter Was Legally Adopted
An adopted daughter has the same rights as a biological daughter, as per the Hindu Adoption and Maintenance Act, 1956.
- The adoption must be legally valid.
- Once adopted, she has the right to inherit her adoptive father’s property.
8. If She Was the Legal Guardian of Her Father
If a daughter took care of her father in his old age, she may get rights under the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007.
- If the father gave her the property while alive or through a will, she can claim it.
- If she was excluded unfairly, she may even ask for compensation from other heirs.
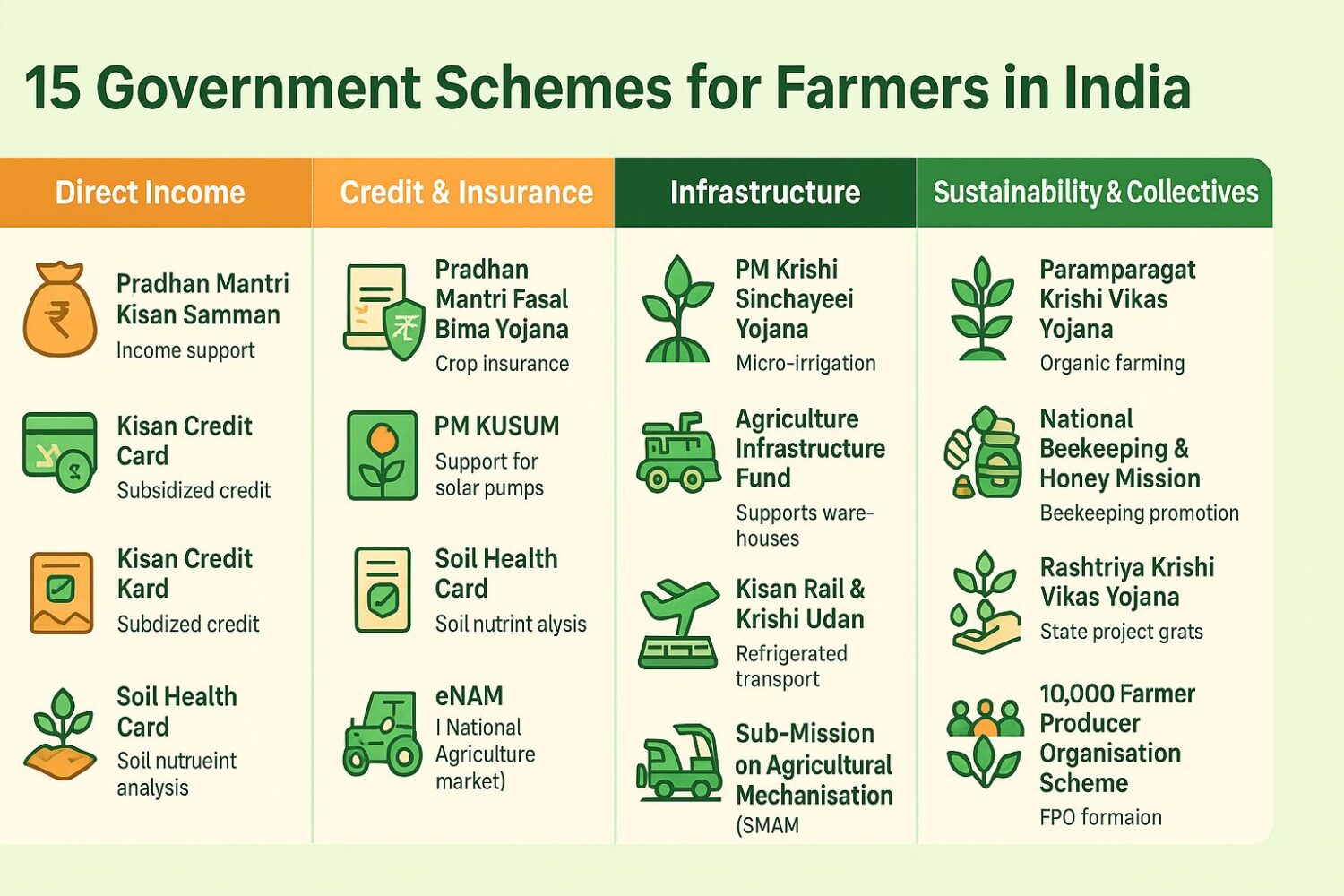
Read More: DPIIT Internship 2025
When Can a Daughter NOT Claim Her Father’s Property?
1. If the Father Left a Valid Will Excluding Her
The father has full rights over his self-earned property. If he names someone else in his will and excludes the daughter, she usually cannot claim anything.
She can only challenge the will if:
- It was forged or fake.
- He was mentally unstable.
- It was made under pressure or influence.
If the will is legally sound, she has no right to claim.
2. If a Legal Partition Happened Before December 20, 2004
Before 2005, daughters didn’t have inheritance rights in ancestral property. If the property was legally divided before December 20, 2004, the daughter cannot ask for a share.
Valid partition means:
- There is a registered legal document, or
- A court officially divided the property.
Note: Oral partitions don’t count. If that’s the only proof, she can still claim her share.
3. If She Converts to Another Religion
The law applies to Hindus, Sikhs, Jains, and Buddhists. If a daughter converts to another religion, she can still inherit. But her children and grandchildren can’t.
Exceptions:
- If she reconverts to Hinduism before the father’s death, she can still inherit.
- If the father names her in his will, she can inherit even after converting.
4. If the Property Came from the Mother With Conditions
Sometimes, the property comes from the mother’s side, and the father inherits it with specific instructions.
- If the mother left a will and excluded the daughter, she can’t claim it.
- If the mother sets conditions (e.g., the property can only go to a son), the daughter’s rights will depend on those conditions.
Read More: Krishak Bandhu Scheme 2025
5. If She Was Adopted Under Special Laws
Normally, adopted daughters have the same rights. But things may be different if:
- The adoption is governed by special rules or community laws.
- There is a personal agreement about property division.
- She is excluded by a legal will—in that case, she can’t claim a share.
6. If Special Rules Apply to the Property
Some properties are governed by special laws. These may not follow regular inheritance rules.
Examples:
- Property under the Indian Succession Act, 1925 (for interfaith marriages).
- Estates of royal families with unique inheritance laws.
- Tribal lands, where traditional rules apply.
If the property falls under these categories, the daughter may not have a right unless she’s clearly mentioned.
7. If She’s Disqualified Due to a Crime or Legal Reason
There are a few serious cases where a daughter can be legally disqualified from inheritance:
- If she’s found guilty of killing or helping kill her father (under Section 25 of the Act), she loses all rights.
- The property then goes to the next eligible legal heir (like the mother or siblings).
Read More: कालिया पोर्टल 2024
Other reasons for disqualification:
- She is declared mentally unfit to handle property.
- She’s found guilty of forging documents or committing fraud related to the property.
Final Words
Thanks to the Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act, 2005, daughters now have equal rights in their father’s property. But it’s not automatic in every case.
There are legal conditions—like wills, past partitions, religious conversions, or disqualifications—that may affect whether a daughter can claim a share or not.
If you or someone you know is having trouble getting their rightful inheritance, the best step is to consult a lawyer. A legal expert can look at the case and suggest the right action based on the situation.
Everyone deserves what’s rightfully theirs—sometimes you just need to know the law and speak up for your rights.
📩 If you notice any incorrect data in this guide or wish to share additional information, please write to us at info@indiansouls.in.
Over 2000+ Government Schemes & Policies Simplified
Indian Souls is your guide to government Schemes, scholarships, pensions, subsidies, job exams, and more. We break complex schemes into easy steps, helping every citizen take full advantage of the opportunities available.
No jargon. No confusion. Just useful info that helps indian citizen.



















![Inheritance & Property Law for Daughters: Claim or Not Claim Her Father’s Property? - Indian Souls 12 Government Schemes for Urban Poor Must Know About [2025 Guide]](https://indiansouls.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/image-1.jpg)